Date: 24 Dec 2026 Read: 21 minutes
1. Executive Summary: The Resilience of Digital in a Contracting Economy
The Thailand market in 2025 presents a complex dichotomy: while the broader advertising sector faces significant macroeconomic headwinds, the digital ecosystem—and specifically the Search Engine Optimization (SEO) sector—demonstrates remarkable resilience and maturation. This report provides an exhaustive analysis of the Thailand SEO landscape, synthesizing data from macroeconomic reports, agency benchmarks, and granular user behavior studies to offer a strategic roadmap for stakeholders.
1.1 Macro-Economic Context and “Small-Joy” Spending
The advertising industry in Thailand contracted by approximately 1.63% in 2025, a deviation from earlier forecasts that predicted a return to growth. This contraction was driven by a confluence of factors: persistent household debt, international trade tensions (specifically “Trump-era tariffs”), and general economic volatility associated with government transitions. Data from “https://www.nationthailand.com/business/corporate/40058492“ In this climate of financial caution, traditional media formats such as television, print, and radio have continued their decline, unable to justify their high costs in an era demanding measurable performance.
However, a critical anomaly exists within this downturn: digital advertising and organic search investments have outperformed expectations. This divergence is attributed to a behavioral shift among Thai consumers known as “small-joy” purchasing. Despite limited purchasing power for large-ticket items, consumers continue to engage in high-frequency online transactions for essential goods, affordable luxuries, and mood-boosting products. This behavior has sustained the e-commerce sector and, by extension, the demand for search visibility. Brands, recognizing that consumer discovery has permanently shifted online, have reallocated budgets from broad-reach traditional channels to performance-driven digital avenues. In this context, SEO has transcended its traditional role as a mere traffic-generation tactic to become a vital mechanism for capturing high-intent demand at a lower Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) than paid media.
1.2 The Strategic Imperative of SEO
As of 2025, SEO in Thailand is no longer an optional “add-on” to marketing campaigns but a fundamental business requirement. The market is characterized by an overwhelming Google monopoly, with the search engine commanding over 99% of mobile traffic with data-based from https://gs.statcounter.com/search-engine-market-share/mobile/thailand. This monopolistic landscape simplifies the platform strategy but intensifies the competition. Visibility on Google is synonymous with digital existence.
Furthermore, the barrier to entry for effective SEO has risen significantly due to regulatory and algorithmic convergence. The Royal Thai Government’s enforcement of digital corporate registration via the Department of Business Development (DBD) and the promotion of the “Thailand Trust Mark” align perfectly with Google’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) guidelines. Technical excellence alone is insufficient; businesses must now demonstrate verifiable digital legitimacy.
1.3 Key Report Findings
The following analysis will detail:
- Mobile Hegemony: With over 90% of web access originating from smartphones, the Thai market is functionally mobile-only, necessitating a radical rethink of “mobile-first” indexing and UX design.
- Linguistic Fluidity: Thai search behavior is defined by code-switching, where users seamlessly blend Thai script, English terms, and transliterated “Karaoke” language within single query sessions.
- The Talent Crisis: A severe shortage of skilled digital labor is driving up agency costs and forcing a rapid adoption of AI technologies to bridge the gap.
- Trust Mechanics: In a low-trust digital environment, external validation through forums like Pantip and government certifications is critical for conversion.
This report serves as a comprehensive guide for navigating these dynamics, offering actionable insights for capitalizing on the 18.4% growth in online travel bookings and the explosive 300%+ ROI reported by mid-sized e-commerce brands investing in SEO based from https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2025-thailand
2. The Digital Consumer: Behavior, Language, and Discovery
Understanding the Thai digital consumer requires moving beyond generic “Southeast Asia” generalizations. The Thai market exhibits unique behavioral patterns driven by high mobile penetration, a distinct linguistic landscape, and a cultural reliance on social validation.
2.1 The Mobile-First Reality
Thailand’s digital population is one of the most mobile-centric in the world. As of 2025, internet penetration exceeds 85%, and mobile devices account for over 90% of all web access. This is not merely a preference but a structural reality; for millions of Thais, the smartphone is the primary and often only gateway to the internet.
Table 1: Internet and Device Usage Statistics (Thailand 2025)
| Metric | Statistic | Strategic Implication |
| Internet Penetration | >85% of population | Digital channels reach near-total saturation of the addressable market. |
| Mobile Web Access | >90% | Desktop optimization is secondary; “thumb-zone” UX is paramount. |
| Mobile Search Share | >70% of all queries | Google’s mobile-first indexing dictates ranking success. |
| Daily Social Usage | 2 hours 58 minutes | High intersection between social discovery and search validation. |
| 5G Rollout | ~90% population coverage | Enables rich media (video) consumption on the go, increasing page weight tolerance. |
The implication for SEO is profound. “Mobile-friendliness” is an outdated metric; the standard is now “mobile-native” experiences. Websites that rely on complex mega-menus, heavy desktop-first interactions, or unoptimized images that drain data plans face immediate rejection. Technical audits reveal that mobile usability issues currently block up to 87% of potential Thai traffic for unoptimized legacy sites. Furthermore, the “Near Me” phenomenon is driven entirely by mobile usage. Hyper-local queries (e.g., “ร้านอาหารใกล้ฉัน” – Restaurants near me) have grown by 150% year-over-year, necessitating a granular approach to Local SEO and Google Maps optimization.
2.2 Linguistic Fluidity and Code-Switching
One of the most challenging aspects of the Thai SEO market is the fluidity of language usage. Unlike markets with a single dominant language, Thai searchers engage in complex code-switching behavior, often within the same search session.
2.2.1 The Three Scripts of Thai Search
- Formal/Standard Thai: Used for official queries, medical advice, and government services. (e.g., “โรงพยาบาล” – Hospital).
- English: Commonly used for brand names, technical terms, luxury goods, and international travel. (e.g., “Digital Marketing Agency”).
- Transliteration (Karaoke Language): Thai words typed in English characters, or English words typed in Thai script. This is prevalent among younger demographics and in chat applications but bleeds into search behavior.
A user journey for a condominium might look like this:
- Step 1 (Broad English): “Condo Sukhumvit”
- Step 2 (Refined Thai): “คอนโด สุขุมวิท ราคาถูก” (Condo Sukhumvit cheap price)
- Step 3 (Validation): “Condo Pantip” (Checking reviews on Pantip forum)
This fluidity means that keyword research tools often underreport the total search volume for a topic because they fragment the data across languages. Effective SEO strategies must target “Hybrid Keywords”—phrases that mix scripts. For example, “ร้านกาแฟ near BTS” (Coffee shop near BTS station) is a high-intent query structure that combines a Thai service noun with an English location modifier.
2.2.2 The “Pantip” Phenomenon
Nowhere is the cultural nuance of Thai search more evident than in the reliance on Pantip.com. Known as the “Reddit of Thailand,” Pantip is not just a discussion forum but a primary validation engine. A significant portion of transactional queries includes the modifier “Pantip.”
- Behavior: Before making a purchase—whether a skincare product, a car, or a condo—a Thai consumer will search “[Product Name] Pantip” to find real user experiences.
- SEO Impact: Often, a Pantip thread will outrank a brand’s own product page for review-related keywords. This requires brands to engage in “Barnacle SEO”—optimizing their presence on third-party sites like Pantip to control the narrative, rather than solely focusing on their own domain.
- Trust Deficit: This behavior stems from a low-trust digital environment where consumers are skeptical of brand claims and seek peer validation. A study indicates that consumers are 60% more likely to choose a business with Thai-language reviews over one with only English reviews, highlighting the critical role of localized social proof.
2.3 Visual and Video Discovery
The Thai market is visually driven. With 87.5% of adults watching short-form videos weekly, the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) is evolving to include more visual elements. Video snippets, particularly from YouTube and increasingly TikTok (indexed by Google), are capturing significant attention.
Data based from https://wearesocial.com/th/blog/2025/02/digital-2025/ and https://hashmeta.com/blog/social-media-landscape-thailand-2025-key-stats-platforms/
- Video Engagement: Thai-language videos receive 3.2x more engagement than static content.
- Ad Format: Video-first creative assets outperform static images by 2x in engagement and 3x in conversion rates.6
- SEO Strategy: This mandates a “Video SEO” strategy. Hosting video content on YouTube with optimized Thai titles, descriptions, and timestamps is essential to occupy SERP real estate. Additionally, optimizing images for Google Lens and visual search is becoming critical as consumers use cameras to search for products they see in the real world.
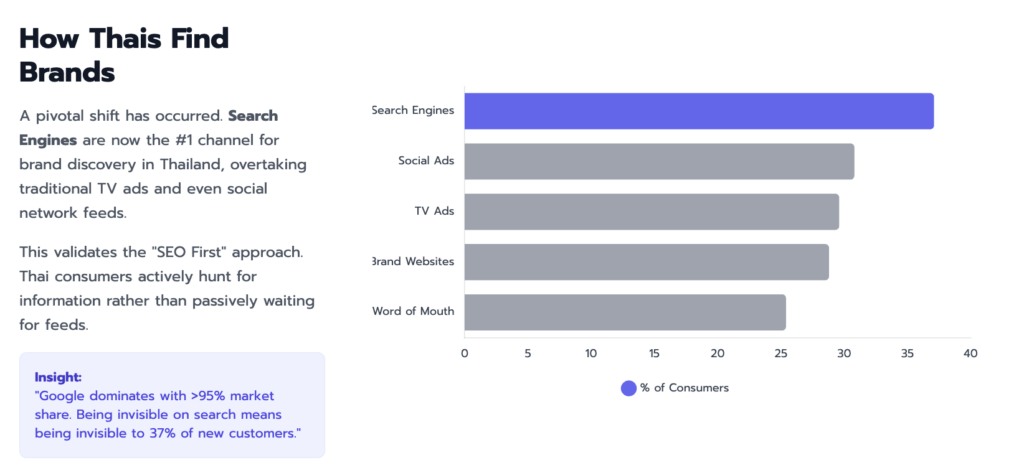
3. Search Engine Market Dynamics and Platform Fragmentation
While Google maintains a statistical monopoly on general web search, the functional definition of “search” in Thailand is fragmenting across vertical platforms. This section analyzes the competitive landscape and the shifting nature of discovery.
3.1 The Google Monopoly
Data from November 2025 confirms Google’s absolute dominance in the Thai market.
Table 2: Search Engine Market Share Overview (Thailand, Nov 2025)
| Search Engine | Total Market Share | Desktop Share | Mobile Share |
| 99.36% | 97.82% | 99.86% | |
| Bing | 0.54% | 2.04% | 0.05% |
| DuckDuckGo | 0.04% | 0.05% | 0.03% |
| Yandex | 0.03% | 0.04% | 0.03% |
Source: Statcounter Global Stats
https://gs.statcounter.com/search-engine-market-share/mobile/thailand , https://gs.statcounter.com/search-engine-market-share/all/thailand , https://gs.statcounter.com/search-engine-market-share/desktop/thailand/%23monthly-202311-202311-bar
Analysis:
- Mobile Monoculture: On mobile devices, Google’s share is effectively 100%. This renders competitors like Bing irrelevant for mass-market consumer strategies. The slight presence of Bing on desktop (2.04%) is likely attributable to corporate IT environments where Microsoft Edge is the default browser.
- Strategy Implication: SEO in Thailand is synonymous with “Google Optimization.” There is no need to diversify technical SEO efforts for other search engines. Resources should be 100% focused on satisfying Google’s ranking signals, specifically Core Web Vitals, Mobile-First Indexing, and E-E-A-T.
3.2 The “Walled Garden” Search Engines
While Google owns the open web, significant search volume occurs inside closed platforms (Walled Gardens).
- Social Search (TikTok & Facebook):
- TikTok: With 32.5 million users and a 35% growth rate since 2023, TikTok has become a primary search engine for Gen Z. Users search for “Bangkok cafe reviews,” “fashion trends,” and “cooking recipes” directly on TikTok. The platform’s algorithm, which favors local content, often provides more relevant, visually rich results than Google for lifestyle queries.
- Facebook: With 50 million users , Facebook serves as a business directory. Many Thai SMEs operate solely via a Facebook Page without a website. Users search Facebook for operating hours, menus, and direct messaging.
- Marketplace Search (Shopee & Lazada):
- Shopee (114 million visits) and Lazada are the default search engines for products. A user looking to buy “running shoes” is more likely to start their search on Shopee than on Google. This necessitates “Marketplace Optimization” (using keywords in product titles and descriptions) as a parallel strategy to web SEO.
- LINE:
- The “Super App” of Thailand with 47 million users. While not a traditional search engine, its “LINE Official Accounts” feature functions as a discovery mechanism. Users search within LINE to find official brand channels for customer service and promotions.
3.3 The Browser Wars
Browser usage dictates the technical constraints of SEO.
- Chrome: Dominates with 69.54% market share.
- Safari: Holds 18.53%, reflecting the high value of the iOS demographic.
- Implication: Technical SEOs must test sites on both Chrome (Blink engine) and Safari (WebKit). Safari’s stricter privacy policies (Intelligent Tracking Prevention) impact analytics data accuracy, making first-party data collection via SEO even more valuable.
4. The Economic Structure of SEO in Thailand: Pricing and ROI
The economics of SEO in Thailand are compelling, particularly when contrasted with the rising costs of paid media. This section benchmarks agency pricing, analyzes ROI, and breaks down costs by industry.
4.1 ROI and Cost Efficiency
In 2025, mid-sized Thai e-commerce brands are reporting average SEO ROIs in excess of 300%, with organic traffic growth rates of 120–150% over a 12-month period. This outsized return is driven by the disparity in Cost Per Acquisition (CPA).
- Paid Media Inflation: CPCs for high-intent keywords in sectors like Real Estate and B2B SaaS have risen to ฿18–฿40 per click.
- Organic Efficiency: The CPA through organic search is typically 60–70% lower than through paid channels.
This efficiency has led to a strategic shift in budget allocation. While paid ads (Google/Social) still command 30-40% of budgets for immediate impact, SEO allocation has grown to 20-30% of total digital marketing spend. 55% of marketers plan to further increase SEO investment in 2026.
4.2 Agency Pricing Benchmarks
The cost of SEO services in Thailand varies widely based on the provider type (freelancer vs. enterprise agency) and the scope of work.
Table 3: SEO Agency Pricing Tiers in Thailand (2025)
| Provider Tier | Monthly Retainer (THB) | Service Scope & Characteristics | Target Client Profile |
| Freelancer / Entry | ฿10,000 – ฿30,000 | Basic on-page optimization, automated reporting, limited keyword tracking. High variability in quality. | Local SMEs, Startups, Personal Brands. |
| Mid-Tier Agency | ฿30,000 – ฿80,000 | Comprehensive keyword research, technical audits, content creation (blogging), manual link outreach, bilingual support. | Mid-sized Corporates, E-commerce, Hospitality. |
| High-End / Enterprise | ฿100,000 – ฿250,000+ | Full-service strategy, Digital PR, deep technical fixes, custom analytics dashboards, dedicated account teams, crisis management. | MNCs, Banks, Large Real Estate Developers, Insurance. |
Source: Clutch Data , https://clutch.co/th/seo-firms
Analysis of Pricing Models:
- Monthly Retainer: This is the most common model, providing predictable costs and ongoing optimization.
- Project-Based: Used for specific tasks like “Technical Site Audit” or “Site Migration.” Costs range from ฿25,000 to ฿200,000 per project.
- Hourly Consulting: Rare, but used by high-level strategists. Rates range from ฿1,500 to ฿5,000 per hour.
- Performance-Based: While attractive to SMEs, reputable agencies generally avoid strict “pay-for-rankings” models due to the unpredictability of algorithms and the risk of black-hat tactics.
4.3 Cost by Industry
SEO costs are not uniform; they are dictated by the competitiveness of the Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
Table 4: Estimated Monthly SEO Investment by Industry (Thailand 2025)
| Industry | Monthly Cost Range (THB) | Drivers of Cost |
| Real Estate | ฿55,000 – ฿200,000+ | Extreme competition for “Bangkok Condo” keywords; high lead value; need for multilingual content (Thai/Eng/Chinese). |
| Travel & Hospitality | ฿55,000 – ฿82,000 | Seasonal strategies; content-heavy (destination guides); visual optimization. |
| SaaS & B2B | ฿55,000 – ฿82,000 | Requires technical expertise; long sales cycles; lead nurturing content. |
| E-commerce | ฿55,000 – ฿150,000 | Technical complexity (thousands of SKUs); duplicate content management; marketplace competition. |
| Healthcare | ฿82,000 – ฿150,000 | YMYL (Your Money Your Life) requirements; need for medical expert writers (E-E-A-T). |
5. Technical SEO: Infrastructure, Challenges, and Solutions
The technical foundation of Thai websites often lags behind global standards, creating both a challenge and an opportunity. Fixing these foundational issues is often the “low-hanging fruit” that drives the fastest initial gains in SEO performance.
5.1 The Legacy Infrastructure Problem
A significant portion of the Thai web operates on legacy infrastructure.
- Hosting Latency: Many Thai businesses host their sites on budget shared hosting in the US or Europe to save costs. Without a Content Delivery Network (CDN), this results in load times of 9–14 seconds for local users.
- The Cost of Speed: For every second of delay after 3 seconds, businesses lose 7% of visitors. Mobile usability issues caused by slow loading block nearly 87% of potential traffic.
- Solution: The expansion of AWS and Google Cloud regions in Thailand offers a solution. Migrating to local cloud infrastructure or implementing a high-performance CDN (like Cloudflare with Bangkok nodes) is a critical Step 1 for any campaign.
5.2 The Thai Font Rendering Issue
A unique technical challenge in Thailand is font rendering.
- The Problem: Thai script requires complex character stacking (tones placed above/below consonants). Standard web fonts often fail to render these correctly or are extremely heavy files (large character sets).
- CLS Impact: As fonts load, they often cause “text shifts” where the layout jumps. This negatively impacts Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), a key Core Web Vital metric.
- Solution: Using modern font formats (WOFF2), subsetting fonts to include only used characters, and implementing
font-display: swapare technical necessities to pass Core Web Vitals assessments.
5.3 Mobile-First Indexing Gaps
Despite Google’s complete transition to mobile-first indexing, many Thai sites suffer from “desktop-centric” architectures.
- Content Parity: It is common for developers to hide content on mobile views to “clean up” the design. Since Google indexes the mobile version, this content is effectively invisible to the search engine, hurting rankings.
- Intrusive Interstitials: Aggressive pop-ups (e.g., “Add Line for Discount”) that cover the screen upon entry are penalized by Google.
- Ghost Pages: 40% of pages on unoptimized sites are often orphaned or non-indexable due to poor mobile navigation structures.
5.4 Legacy CMS and Script Bloat
Many Thai websites use outdated Content Management Systems (CMS) or heavily customized WordPress themes that are bloated with tracking scripts.
- Script Overload: A typical e-commerce site might have Facebook Pixel, TikTok Pixel, Line Tag, Google Analytics, Google Ads, and Hotjar all firing simultaneously. Without a Tag Management System (GTM), this freezes the browser, specifically on mid-range smartphones common in Thailand.
- Security: 88.8% of global sites use HTTPS, but legacy Thai sites often miss SSL certificates, triggering “Not Secure” warnings that destroy trust.
6. Trust, Authority, and E-E-A-T Strategies
In 2025, Trust is the currency of the Thai internet. Google’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) framework is applied rigorously, especially for YMYL sectors.
6.1 The “Trust Deficit” and Official Certifications
Thai consumers are naturally skeptical of online claims due to a history of scams and counterfeit goods. To counter this, “Trust Signals” are essential for both conversion and SEO.
6.1.1 Thailand Trust Mark (TTM)
The Thailand Trust Mark (TTM), endorsed by the Royal Thai Government (Department of International Trade Promotion), is a powerful signal.
- SEO Impact: While the mark itself isn’t a direct ranking factor, the entity association is. Being listed in the official government directory provides a high-authority backlink (.go.th domain).
- Conversion: Displaying the TTM logo assures consumers of labor standards, environmental responsibility, and quality, leading to higher on-site engagement metrics (time on site), which indirectly boosts SEO.
6.1.2 DBD Biz Regist
Effective July 1, 2025, the Department of Business Development (DBD) mandates digital corporate registration via “DBD Biz Regist”.
- Verification: Displaying the DBD Registered badge validates the legal existence of the company. Smart SEOs use Schema Markup to link this verification to the website’s “Organization” schema, explicitly telling Google, “This is a verified, legal entity.”
6.2 Building Authority (The “A” in E-E-A-T)
Authority in Thailand is built through association with established media and institutions.
- Digital PR: Securing mentions in Tier-1 Thai media (Bangkok Post, Thairath, Sanook) is more valuable than hundreds of low-quality directory links. These sites have massive domain authority and traffic.
- Influencer Citations: When a credible influencer (or “Guru”) mentions a brand in a blog or video, it creates a “co-citation” that strengthens the brand’s entity graph.
6.3 Experience (The “E” in E-E-A-T)
Google’s “Experience” update rewards content that demonstrates first-hand knowledge.
- Original Imagery: For travel and food, using stock photos is a negative signal. Authentic, even imperfect, photos taken by the author prove “I was there”.
- Authorship: Articles should be bylined by real people with bio pages that list their credentials. “Admin” or “Staff” bylines are penalized in rankings for medical or financial content.
7. Industry-Specific SEO Deep Dives
7.1 Real Estate: The High-Stakes Battlefield
Real Estate is the most competitive SEO vertical in Thailand due to high transaction values.
- Challenge: CPCs are high (฿18–฿35+), and aggregators (DDproperty, Dot Property) dominate broad keywords like “Bangkok Condo.”
- Strategy: Hyper-local SEO. Instead of “Bangkok Condo,” optimized for “Condo near BTS Thong Lo” or “Pet-friendly condo Ari.” These long-tail keywords have lower volume but extremely high intent.
- Chinese SEO: With strong demand from Chinese investors, high-end developers must also optimize for Baidu (using simplified Chinese) or optimize their Google content for Chinese keywords searched by expats.
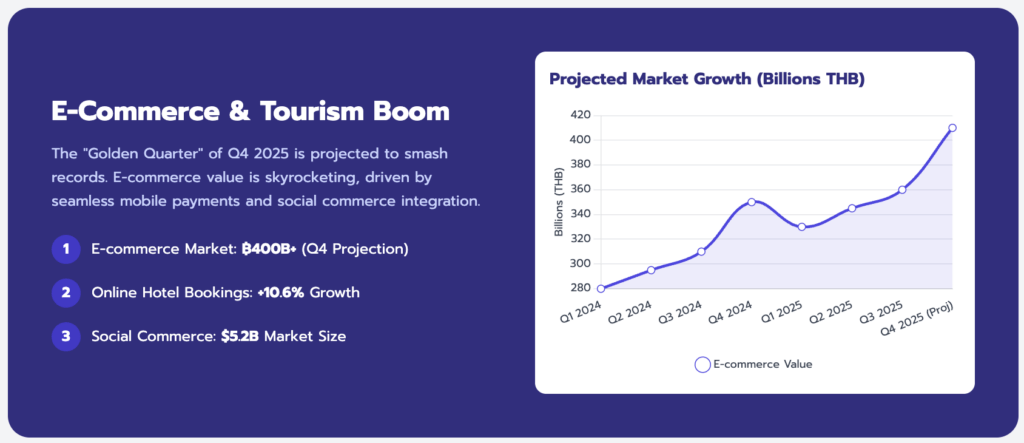
7.2 Tourism and Hospitality
- Recovery: Online flight bookings grew 6.3% and hotel bookings 10.6% in 2024/25.
- Bilingual Strategy: Hotels need a dual strategy. English content targets high-value international tourists (high CPC), while Thai content targets the domestic “staycation” market.
- Visual SEO: High-quality images and video tours are non-negotiable. Google Travel features rely heavily on visual structured data.
7.3 E-commerce
- Marketplace vs. Brand.com: Brands fight a losing battle against Shopee/Lazada for product keywords.
- The “Category” Defense: Smart brands focus on ranking their Category Pages (e.g., “Best Running Shoes 2025”) and Informational Blogs (“How to choose running shoes”), areas where marketplaces often have thin content.
- Conversion Benchmarks: Personal Care converts at a high 6.8%, while Home Decor lags at 1.4%. SEO strategies for low-conversion sectors must focus on “Trust Building” content (warranties, reviews, specs) to aid the decision process.
7.4 B2B and Industrial
- The EEC Factor: The Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) drives demand for industrial keywords. Suppliers optimizing for “Factory automation Chonburi” or “Warehouse rental EEC” are capturing high-value B2B leads.
- LinkedIn Integration: For B2B, SEO works in tandem with LinkedIn. Ranking for “Corporate Services Thailand” often leads to a LinkedIn profile check.
8. The Talent Crisis and the Role of AI
A critical constraint in the 2025 market is the shortage of skilled digital talent.
8.1 The Shortage
- Upskilling Gap: While 74% of workers have access to learning resources, there is a disconnect between academic training and practical SEO skills.
- Rising Costs: The scarcity of “Head of SEO” or “Technical SEO Specialist” roles has driven salaries up, forcing agencies to increase fees or rely on junior staff.
Based on https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/thailand-digital-transformation-market
8.2 AI as the Bridge
To bridge this gap, AI adoption in Thailand has surged.
- Usage: 72% of Thai workers used AI in their jobs in the past year, significantly higher than the global average of 54%.
- Agency Application: Agencies use Generative AI for:
- Content Scaling: Drafting descriptions for thousands of e-commerce SKUs.
- Data Analysis: Using AI to analyze log files and crawl data for technical audits.
- Keyword Clustering: Grouping thousands of keywords into semantic topics.
- Risk: The danger is “AI Spam.” Google’s algorithms are aggressively penalizing unedited, low-value AI content. The winning formula is “AI-Drafted, Human-Refined,” ensuring the “Experience” element of E-E-A-T is added by a human editor.
9. Future Outlook: Trends for 2026 and Beyond
9.1 AI Search (SGE) and Zero-Click
Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) is changing traffic patterns. Informational queries are increasingly answered on the SERP, leading to a decline in traffic for “Definition” style keywords.
- Entity Optimization: Brands must focus on becoming an “Entity” in Google’s Knowledge Graph so that AI mentions them in the generated answer.
- Shift to Transactional: As informational traffic dips, the value of transactional keywords (which trigger product listings) increases.
9.2 PDPA and First-Party Data
As privacy laws tighten, “rented” audiences (Facebook pixels) become less reliable.
- SEO Asset: Organic traffic builds a First-Party Data asset. Capturing emails via SEO content allows brands to own their audience, insulating them from platform policy changes.
9.3 Voice Commerce
Voice search will evolve into Voice Commerce. Users will not just ask “Where is a flower shop?” but “Order flowers from.” This requires consistent NAP (Name, Address, Phone) data across the entire digital ecosystem.
10. Strategic Recommendations
To succeed in the Thailand SEO market in 2025, we recommend the following strategic pillars:
- Adopt a “Thainess” Content Strategy: Move beyond translation. Invest in native content creation that understands code-switching, cultural nuances, and the appropriate level of formality.
- Obsess Over Mobile Performance: Treat your mobile site as your only site. Audit for speed, touch targets, and content parity. If it doesn’t work on a mid-range Android phone on 4G, it doesn’t work.
- Build Verifiable Trust: Acquire the Thailand Trust Mark, display your DBD registration, and actively manage your reputation on Pantip and Google Maps.
- Diversify Discovery: While Google is king for search, ensure your brand is visible on TikTok and Shopee to capture the “discovery” phase of the journey.
- Invest in Hybrid Talent: Build teams that combine AI proficiency with deep strategic understanding. AI can write the code, but a human must define the strategy.
Conclusion
The Thailand SEO market is vibrant, lucrative, and unforgiving. It rewards brands that respect its unique cultural and technical landscape. By pivoting to a mobile-first, trust-based, and linguistically fluid strategy, businesses can secure a dominant position in Southeast Asia’s most dynamic digital economy.




